In the competitive beverage industry, efficiency is the heartbeat of success. Whether you are producing craft soda, premium water, or vintage wine, the speed and accuracy of your packaging define your market capability. Complete bottling systems are the engine behind this productivity, transforming raw liquid into shelf-ready products with precision. Bottle filling is no longer just about pouring liquid into a container; it is a sophisticated dance of engineering and hygiene. This blog post explores the essential components, detailed processes, and strategic benefits of modern bottling line solutions, guiding you toward optimizing your production for maximum output and quality.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Bottling Lines
Bottling lines are the backbone of efficient beverage production, seamlessly transforming raw liquids into packaged products ready for distribution. To fully understand their value, it’s essential to explore how these systems work and the components that make them so effective. From the initial cleaning of containers to the final packaging stages, each element of a bottling line is designed to optimize productivity and maintain product quality. Let’s take a closer look at what defines a bottling line and the critical equipment that drives its success.
What is a Bottling Line?
A bottling line is an integrated sequence of machines designed to process beverages from a holding tank to a finished, packaged product. These automated bottling systems handle every step of the bottling process, including washing, filling, capping, labeling, and packaging. The primary purpose of a bottling line is to ensure high-speed production while maintaining consistent quality and strict hygiene standards. By automating these tasks, manufacturers can achieve throughput levels that manual labor cannot match, providing scalability and efficiency.
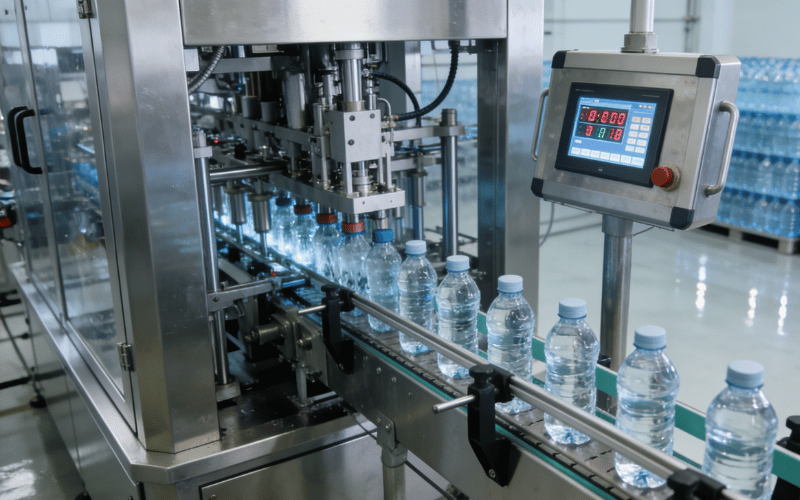

Components of a Bottling Line
A successful line relies on synchronized bottling line equipment. Each component plays a vital role in moving the product forward efficiently:
- Rinsers: These machines clean bottles to remove dust and contaminants before filling begins.
- Filling Machines: The core of the system, these dispense exact liquid volumes into containers.
- Capping Machines: These secure bottles with caps or corks to seal in freshness.
- Labeling Machines: These apply branding and regulatory information to the exterior of the bottle.
- Conveyors: These transport bottles smoothly between different stations to prevent bottlenecks.
Importance of Used Bottling Lines
For startups and small businesses, the cost of new machinery can be prohibitive. Investing in used bottling equipment offers a practical alternative. Affordable bottling solutions allow emerging brands to access professional-grade technology without the massive initial capital expenditure. High-quality used lines are often refurbished to meet current standards, providing a sustainable option that extends the lifecycle of industrial machinery. By choosing used equipment, businesses can allocate more resources to marketing and product development while still ensuring reliable production capabilities.
Types of Bottling
When it comes to bottling, the type of container and the production method play a significant role in determining efficiency, cost, and consumer appeal. From the choice between glass and PET containers to the decision between automated and manual bottling systems, each option has its own set of advantages and trade-offs. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right solution for your production needs. Let’s dive deeper into the various types of bottling and explore how they cater to different industries and product requirements.
Glass Bottles vs. PET Containers
The choice between glass vs. PET bottling impacts everything from logistics to consumer perception. Glass offers a premium feel and infinite recyclability, while PET provides lightweight durability and lower transport costs.
|
Feature |
Glass Bottles |
PET Containers |
|---|---|---|
|
Durability |
Fragile, requires careful handling. |
High impact resistance, shatterproof. |
|
Sustainability |
Infinite recyclability, heavy transport footprint. |
Recyclable, lightweight lowers carbon emissions. |
|
Cost |
Higher material and shipping costs. |
Lower production and logistics expenses. |
|
Perception |
Premium, traditional, high-quality. |
Convenient, modern, on-the-go. |
Automatic Bottling vs. Manual Bottling
Choosing between automated bottling systems and manual bottling processes depends largely on your production scale and budget.
- Automatic Bottling:
- Pros: Extremely high speed, consistent fill levels, lower long-term labor costs.
- Cons: High initial investment, requires technical maintenance skills.
- Manual Bottling:
- Pros: Low startup cost, flexible for very small batches, easy to operate.
- Cons: Slow production rate, higher risk of inconsistency and human error, labor-intensive.
Specialized Lines for Wine Bottling
Wine bottling lines require specific features to preserve the integrity of the vintage. Unlike standard water or juice lines, these specialized bottling solutions must manage oxidation risks carefully. Key features often include nitrogen flushing systems that displace oxygen from the empty bottle before filling. Additionally, corking machines must handle natural or synthetic corks with precision to prevent taint. Some lines also incorporate bottle-aging capabilities or specific gentle-handling conveyors to ensure the wine is not excessively agitated before it reaches the consumer.
Bottling Process Overview
The bottling process is a carefully orchestrated sequence of steps designed to ensure efficiency, precision, and product integrity. Each stage, from filling to sealing and labeling, plays a vital role in delivering a high-quality product to the consumer. By understanding the function of each machine in the bottling line, manufacturers can optimize their operations and maintain consistent results. Let’s take a closer look at the key components of the bottling process, starting with the filling machines that form the foundation of any successful production line.
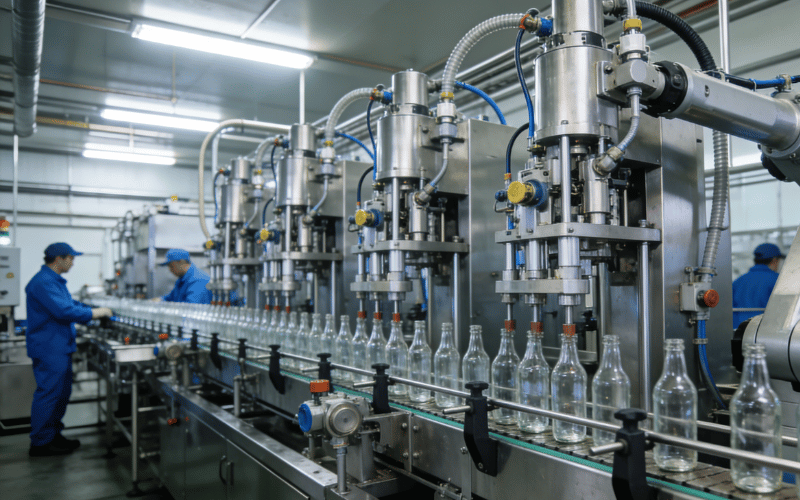
Filling Machines in the Bottling Process
Bottle-filling machines are the heart of the operation, tasked with ensuring liquid-filling solutions are delivered quickly and accurately. The type of filler depends on the liquid’s viscosity and carbonation. Gravity fillers are ideal for thin, non-carbonated liquids like water and wine, using the liquid’s weight to fill the bottle. Piston fillers work best for thick products like sauces or heavy creams. Advanced volumetric fillers ensure that every bottle contains the same amount of product, minimizing waste and ensuring compliance with packaging regulations.
Capping Machines: Ensuring Seal Integrity
Once filled, the bottle must be sealed immediately. Capping machines are critical for maintaining seal integrity, which protects the product from contamination and spoilage. These machines apply the closure with a specific torque to ensure a tight fit. The method varies by product: screw caps are standard for sodas and waters, while crown caps are standard for beer. Proper capping prevents leaks during transport and ensures that the beverage reaches the customer in the condition the brewer or vintner intended.
Labeling Machines: Enhancing Product Presentation
The label is the face of your brand. Labeling solutions do more than provide nutritional data; they create shelf appeal. Modern machines can apply pressure-sensitive labels, cold glue labels, or full-body shrink sleeves that conform to unique bottle shapes. High-quality labeling ensures that branding is aligned perfectly and free of wrinkles or bubbles. This attention to product presentation is crucial, as the label is often the deciding factor for a consumer browsing a crowded store shelf.
Packaging Solutions in Bottling
Beyond the core bottling process, effective packaging solutions are essential for ensuring product safety, quality, and consumer appeal. From extending shelf life with pasteurization to maintaining hygiene with advanced cleaning systems, packaging plays a pivotal role in the success of any bottling operation. By integrating these solutions into the production line, manufacturers can enhance efficiency, meet regulatory standards, and deliver products that exceed customer expectations. Let’s explore the critical packaging components that elevate bottling lines to the next level.
Role of Pasteurizers in Beverage Packaging
For many beverages, shelf life and safety are paramount. This is where pasteurization in bottling plays a critical role. Tunnel pasteurizers spray hot water over filled and sealed bottles to kill potential spoilage organisms and pathogens. This process ensures beverage safety without the use of chemical preservatives. It is commonly used for beer, juices, and energy drinks. By integrating pasteurization into the line, producers can guarantee a stable product that remains safe for consumption over long periods, protecting both consumers and brand reputation.
Using CIP in Bottling Lines
Hygiene is non-negotiable in beverage production. CIP systems (Clean-in-Place) are automated cleaning methods that circulate sanitizing solutions through the internal pipes, pumps, and valves of the bottling line without disassembly. Regular bottling line cleaning prevents bacterial growth and cross-contamination of flavors between batches. CIP ensures that every run starts in a sterile environment, meets strict food safety regulations, and reduces the downtime typically required for manual cleaning processes.
Customer Satisfaction in Packaging
Ultimately, the goal of any production line is a happy consumer. Efficient bottling lines directly contribute to customer satisfaction in bottling by delivering a consistent, safe, and attractive product. When a customer picks up a bottle, they expect the fill level to be correct, the seal to be intact, and the label to be straight. Packaging quality reflects the quality of the liquid inside. A reliable bottling line ensures that every unit leaving the factory meets these high standards, building trust and loyalty with your customer base.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common types of bottling lines, and how do they differ?
Common types of bottling lines include gravity filling, pressure filling, and monoblock systems; gravity filling is ideal for water bottling and low-viscosity liquids, pressure filling suits carbonated or sparkling water and beverages with carbonation, while monoblock lines integrate filler, cap, and labeler in a single state-of-the-art machine to minimize manual intervention. Lines for PET and glass bottles (glass and PET) require different handling, capping, and accumulation solutions to protect product quality and meet production goals.
How does automation in bottling equipment improve production capacity and reduce costs?
Automation and state-of-the-art technology in bottling equipment and packaging machines increase throughput of bottles per minute, reduce labor costs, and minimize downtime through predictive maintenance and modular design. Automated accumulation tables and inline accumulation help maintain production flow during intermittent stops, improving scalability and reducing waste and overall production costs while achieving consistent traceability for every bottle.
What role do the filler and filling lines play in product quality and shelf life?
The filler is central to filling and packaging; correct pressure filling or gravity filling methods, combined with inert gas flushing for oxygen-sensitive products, prevent oxidation and contamination, preserving product quality and extending shelf life. High-performance fillers, integrated with hygienic line equipment and cleaning protocols, are essential in beverage production to maintain shelf stability and sparkle for sparkling water and carbonated beverages.
How do cappers, screw caps, and closure systems affect packaging integrity?
Cappers and closure systems, including screw caps and bottle caps, ensure seal integrity and prevent leaks, contamination, and CO2 loss in carbonated drinks. Choosing the proper closure and synchronized bottling machine reduces cap-related rejects and supports traceability; some systems include tamper-evident features and are compatible with downstream carton and pallet packing.
What should a production facility consider when selecting a supplier for bottling machinery?
Select a supplier that provides state-of-the-art technology, complete packaging systems, and after-sales support. Essential factors include scalability, adaptability to specific product types (e.g., viscous syrups, carbonated or still water), availability of spare parts, training, and services to minimize downtime. A strong supplier will help interconnect the entire process from the syrup room and premix to the pasteurizer and final carton packing to meet unique production requirements.
How can bottling lines minimize waste, energy consumption, and carbon footprint?
Minimizing waste and energy consumption involves optimizing line equipment to reduce rejects, using energy-efficient motors and drives, implementing inline inert gas use only when needed, recovering heat from pasteurizers, and automating changeovers to reduce product loss. Efficient pallet and carton packing, accurate fillers to minimize overfills, and process control that meets production goals also reduce production costs and carbon footprint.
What is the importance of hygiene and traceability in bottling operations?
Strict hygiene practices and hygienic machinery design are vital to prevent microbial contamination and maintain product quality; clean-in-place (CIP) systems, sanitary fillers, and controlled syrup room practices are standard. Traceability systems integrated into packaging machines record batch data for every bottle, enabling recalls, quality audits, and compliance with food safety regulations.
How do bottling lines handle different bottle types and unique production needs?
Flexible line equipment with adjustable starwheels, grippers, and change parts enables handling of glass and PET bottles of different sizes. For viscous products or premix syrups, specialized fillers and pumps ensure accurate dosing. Accumulation tables and modular conveyors facilitate smooth production flow and quick format changes, supporting unique production runs and mixed SKU lines with minimal need for manual intervention.
What maintenance and operational strategies help maximize uptime and performance?
Implement preventive maintenance schedules, operator training, and spare-parts inventory to minimize downtime. Use state-of-the-art monitoring for inline sensors and diagnostics, plan for regular cleaning of fillers and cappers, and adopt predictive analytics where possible. Efficient layout and accumulation to absorb stoppages, plus coordination between filling and packaging machines, maintain high performance and help meet production capacity and goals.
Conclusion
Investing in robust bottling line solutions is a strategic move for any beverage manufacturer. From the precision of filling machines to the reliability of capping and labeling units, every component contributes to a more efficient and profitable operation. Whether you choose new automated systems or cost-effective used equipment, the proper setup will elevate your production capabilities. Ready to optimize your process? Contact us to learn more about bottling solutions tailored to your specific needs.




